2020/09/17
Exoskeleton
Bus Magnetic Ring Encoder case
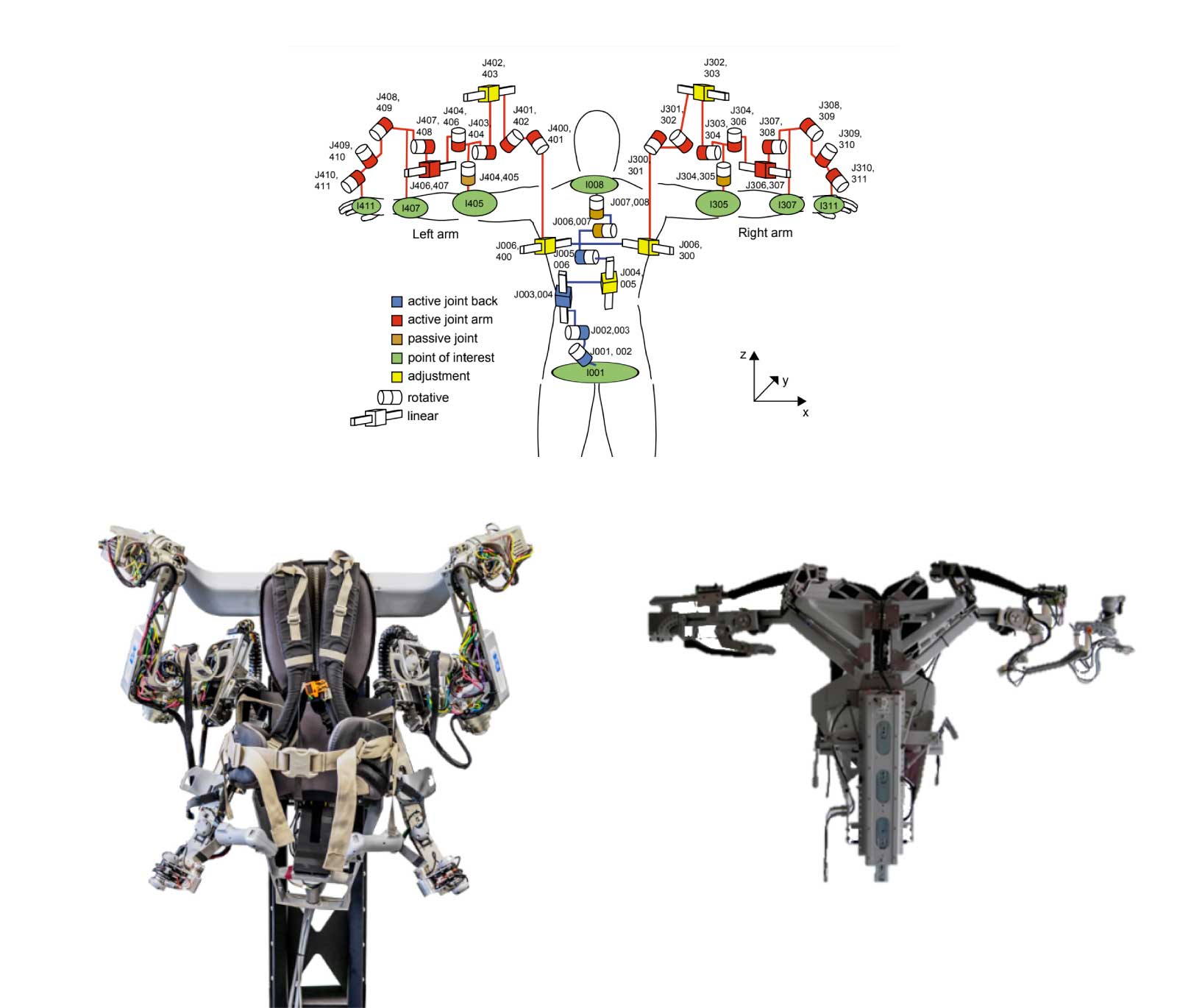
As more robot applications emerge, their working modes become increasingly specialized. According to different scenarios, they are mainly divided into the following types:
- Autonomous operation: The robot runs pre-set programs independently without user intervention.
- Collaborative operation: The robot works with user intervention, learning in real time through guided teaching.
- Manual operation: The robot is fully controlled and operated by the user.
The three modes serve different purposes. Autonomous mode handles repetitive tasks with simple mechanical design. Collaborative mode requires joint force sensing for drag teaching, which is not needed in autonomous systems.
Manual operation:
Manual operation is fully user-controlled, with the human hand replaced by a mechanical actuator. This allows for functions beyond direct human capability and supports the use of specialized actuators for different tasks.
- Force: Enables output greater or smaller than human strength — such as heavy-duty palletizing robots or precision surgical robots.
- Reach: Enables operation in places inconvenient or unreachable for human hands, such as bomb disposal robots, high-voltage line inspection, and endoscopic robots.
- Accuracy: Delivers accuracy beyond human capability, such as in surgical robots.
The case referenced in this article issantificThe company’s products mainly enable remote delivery and operation of actuators to perform high-risk tasks such as bomb disposal and high-voltage line inspection. Moving beyond traditional remote control boxes with buttons and knobs, ShenTuo Technology is exploring more user-friendly control methods, leading to the development of their exoskeleton-style controller.:
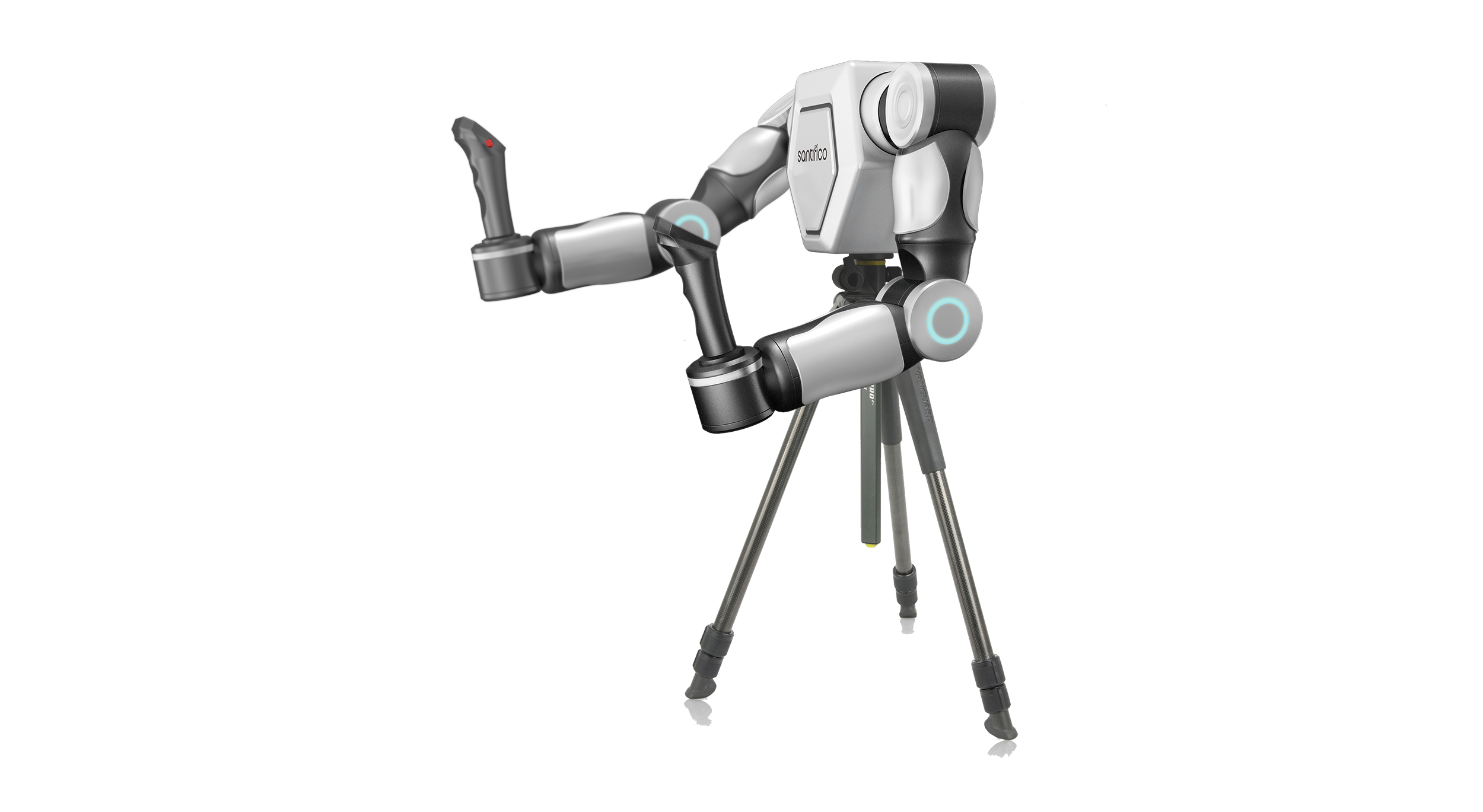

The exoskeleton controller closely integrates with the human body, fully replicating arm movements onto the actuators. Compared to traditional remote control boxes, this operation mode is more intuitive, easier to learn, and highly efficient. Below is a demonstration of the product in use:
Exoskeleton Controller
For the exoskeleton controller, control of the robot’s actions is achieved by sensing human limb movements. This precise motion sensing is realized through multiple bus magnetic ring encoders, as shown in the figure below:
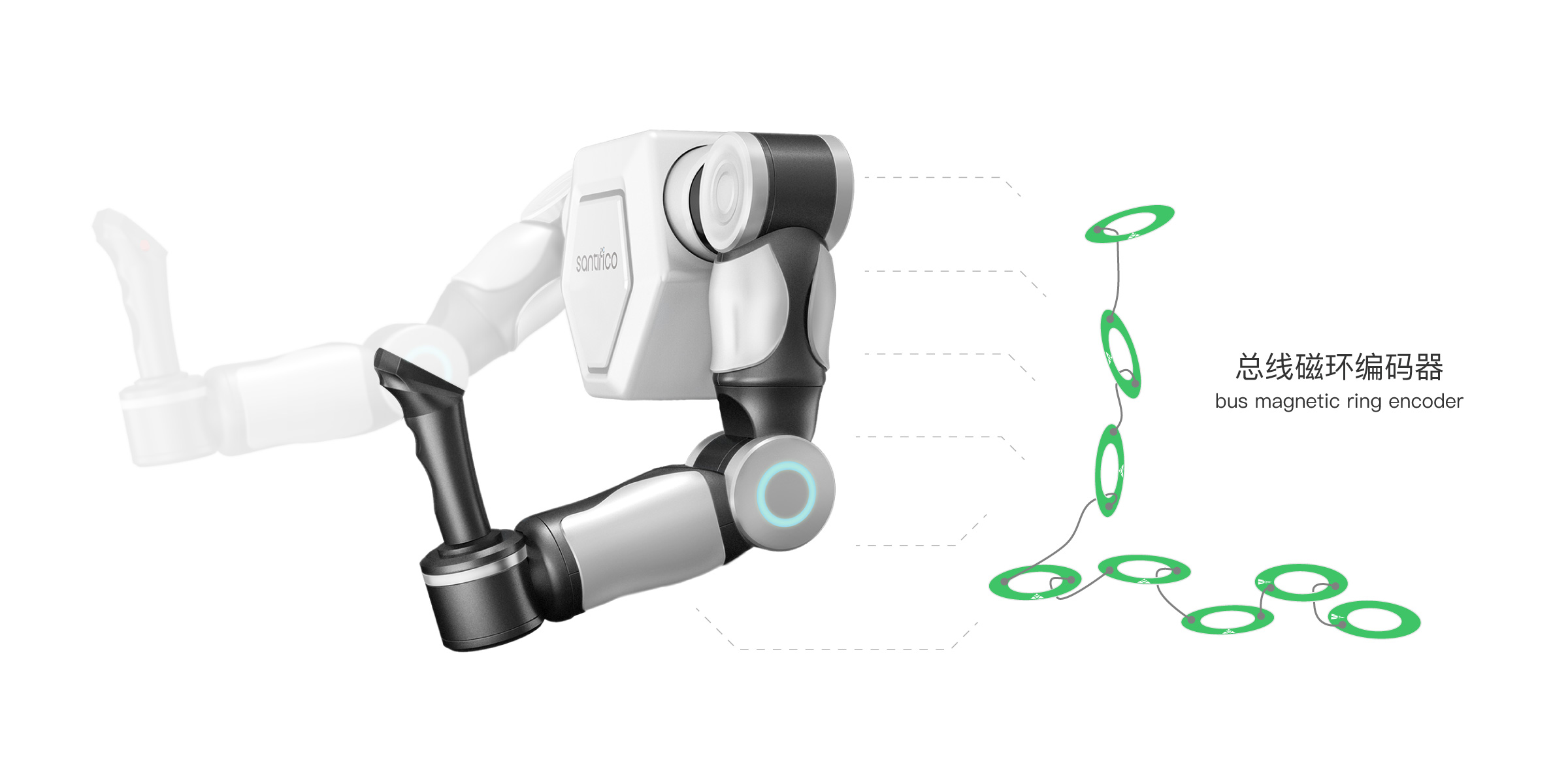
There are three design solutions for the exoskeleton controller:
- Motion sensing
- Motion sensing + Passive damping
- Electric drive force control
These three solutions can be selected based on the degrees of freedom and actual application requirements.
Of theseMotion sensingThe most convenient and flexible, uniquely offering ease of use and excellent overall cost-performance.Passive DampingLike a double-edged sword, it improves some minor control effects but reduces control agility and the overall tactile experience.Electric drive force controlHigh cost and complex system; good control performance but limited by application environment, making it unsuitable for widespread use.
Therefore,Motion sensing can be the preferred solution for designing skeletal-style controllers., Continuously refining operations with real-time feedback from vision and specialized sensors.
Bus Magnetic Ring Encoder
As a device that interacts directly with the human body, a skeletal-style controller must minimize size and weight, be easy and compact to operate, and achieve high-precision real-time detection of human movements. Therefore, the encoder requirements are as follows:
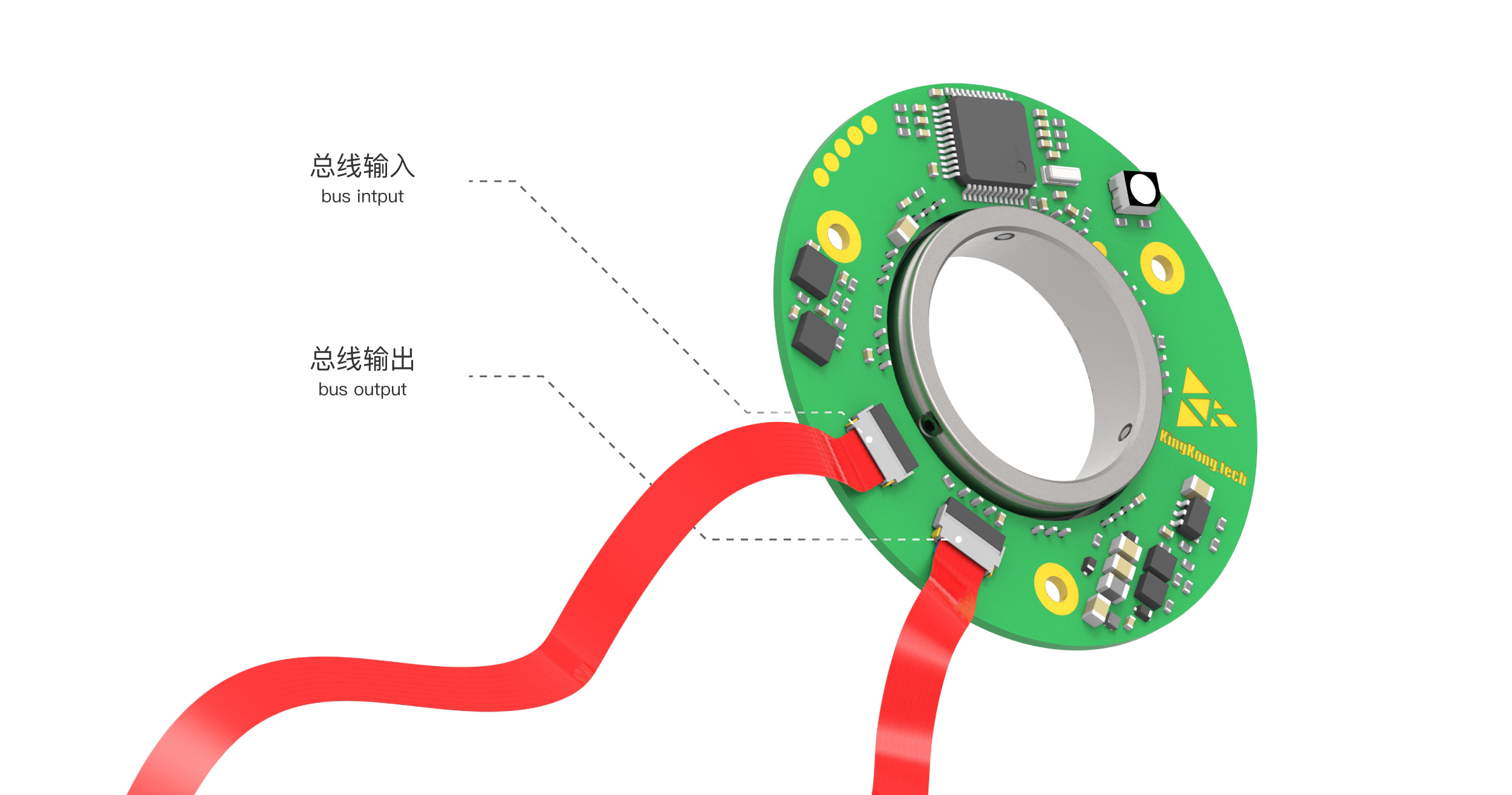
- Hollow: Hollowness allows all wiring to pass through the exoskeleton body without being exposed outside, preventing direct contact with the human body and avoiding safety risks.
- Ultra-thin: A thin and lightweight design makes the overall structure more compact, better suited to the human body's carrying capacity, and easier to handle.
- Bus: All encoders share a common bus for power and communication in a daisy-chain configuration, resulting in a simpler design and improved scalability.
- High-speed: To reliably achieve real-time performance, the bus must simultaneously read angle data from multiple encoders with very high communication speed and security.
- High precision: Accurate measurement of the angles input by the human body to the exoskeleton is essential for precise operation.
Kingkong Technology’s bus magnetic ring encoders meet diverse application needs, featuring an angle measurement core that can be...MBS、MBPIt supports Kingkong Technology’s proprietary high-speed bus protocol or Modbus, among others, offering strong scalability and enabling fast, secure communication with your other functional modules on the bus beyond just measurement.
The above is a case study of bus magnetic ring encoders for mechanical exoskeletons. If you have any questions or need assistance, please feel free to contact us.
